
Study the table with
the rules and then do the exercises.
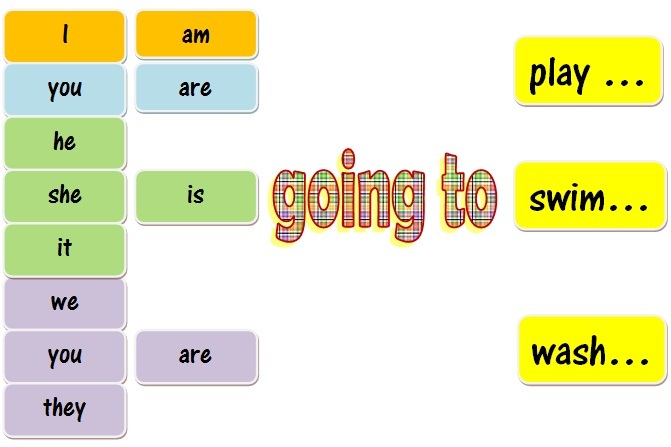
•She
going to have a birthday party. •Tom going to pass his
exams.
•I
going to make sausages for lunch. • They going to go to
England.
•My sister going to do her English Homework.•
It going to fall down.

•Emma
her English exam next
week.
•It is very hot today. I in the lake.
•We our grandparents this weekend. We haven't seen them for a long
time.
•John and his brother their bikes.
•I the table. It's
time for lunch.
•David his homework
after school.
•It's Paul's birthday next week. We him a present.
•His sister the
violin at the concert.
| ||||||||||||||||
- Verb Tense Final Test Cumulative Verb Tense Review
Gramática
Should | ||
COMPARATIVES AND SUPERLATIVES
En inglés cuando comparamos dos cosas usamos los adjetivos y sus tres grados: positivo, comparativo y superlativo. Aquí tienes algunos ejemplos.
Grados de los Adjetivos
Los adjetivos tienen tres grados de comparación.Grado positivo, grado comparativo, grado superlativo:
| positivo | comparativo | |
|---|---|---|
| tall alto | taller más alto | the tallest el más alto |
| big grande | bigger más grande | the biggest el más grande |
| intelligent inteligente | more intelligent más inteligente | the most intelligent el más inteligente |
| expensive caro | more expensive más caro | the most expensive el más caro |
- John is tall, but Bill is taller than John.
John es alto pero Bill es más alto que John. - Jack is very tall. He is the tallest man in the team.
Jack es muy alto. El es el hombre más alto del equipo.
Adjetivos Monosílabos - Formación del Comparativo y Superlativo
| Monosílabos | Comparativo adj + er | adj + est |
|---|---|---|
| small pequeño | smaller más pequeño | the smallest el más pequeño |
| tall alto | taller más alto | the tallest el más alto |
| young joven | younger más joven | the youngest el más joven |
| old viejo | older más viejo | the oldest el más viejo |
| new nuevo | newer más nuevo | the newest el más nuevo |
| long largo | longer más largo | the longest el más largo |
| short corto | shorter más corto | the shortest el más corto |
| big grande | bigger más grande | the biggest el más grande |
| fat gordo | fatter más gordo | the fattest el más gordo |
Adjetivos Bisílabos - Formación del Comparativo y Superlativo
Bisílabos terminados en: -y, -er, -le, -ow, (y otros muy conocidos)| Bisílabos | Comparativo adj + er | adj + iest |
|---|---|---|
| easy fácil | easier más fácil | the easiest el más fácil |
| happy feliz | happier más feliz | the happiest el más feliz |
| crazy loco | crazier más loco | the craziest el más loco |
| clever inteligente | cleverer más inteligente | the cleverest el más inteligente |
| tender tierno | tenderer más tierno | the tenderest el más tierno |
| humble humilde | humbler más humilde | the humblest más humilde |
| gentle suave | gentler más suave | the gentlest el más suave |
| narrow angosto | narrower más angosto | the narrowest el más angosto |
| polite amable | politer más amable | the politest el más amable |
Adjetivos Largos - Formación del Comparativo y Superlativo
| Adjetivos Largos | Comparativo more + adj | the most + adj |
|---|---|---|
| expensivecaro | more expensivemás caro | the most expensiveel más caro |
| modernmoderno | more modernmás moderno | the most modernel más moderno |
| beautifulhermoso | more beautifulmás hermoso | the most beautifulel más hermoso |
| elegantelegante | more elegantmás elegante | the most elegantel más elegante |
| interestinginteresante | more interestingmás interesante | the most interestingel más interesante |
| dangerouspeligroso | more dangerousmás peligroso | the most dangerousel más peligroso |
Formación irregular de comparativos y superlativos
| Adjetivo o Adverbio | Comparativo | |
|---|---|---|
| good bueno | better mejor | the best el mejor |
| well bien | better mejor | the best de la mejor forma |
| bad malo | worse peor | the worst el peor |
| badly mal | worse peor | the worst de la peor forma |
| much mucho | more más | the most la mayor parte |
| many muchos | more más | the most la mayoría |
| little poco | less menos | the least el menos |
| far lejos | farther más lejos | the farthest el más lejano |
| far lejos | further más lejos | the furthest el más lejano |
Adjectives
TERCER PERIODO
The Past Continuous
El 'past continuous' o 'past progressive' se emplea para acciones pasadas en proceso de realización. Es decir, lo que ocurría o estaba ocurriendo en el pasado.
I was having lunch at 2 o’clock. - Estaba comiendo a las 2.
What were you doing when I phoned? - ¿Qué estabas haciendo cuando llamé?
They weren’t sitting in the restaurant when we arrived. - No estaban sentados en el restaurante cuando llegamos.
Se forma con el pasado del auxiliar to be + el verbo+ing
I was (was=el pasado del verbo to be) having (el verbo 'have' + ing) lunch.
Se puede emplear el past continuous y el past simple juntos. En este caso, el past continuous se usa para la acción más larga y el past simple para la acción más corta.
We were driving along when suddenly a dog ran out in front of the car.
She sent (past simple) me a text message while I was waiting (past continuous) for her.
I was having lunch at 2 o’clock. - Estaba comiendo a las 2.
What were you doing when I phoned? - ¿Qué estabas haciendo cuando llamé?
They weren’t sitting in the restaurant when we arrived. - No estaban sentados en el restaurante cuando llegamos.
Se forma con el pasado del auxiliar to be + el verbo+ing
I was (was=el pasado del verbo to be) having (el verbo 'have' + ing) lunch.
Se puede emplear el past continuous y el past simple juntos. En este caso, el past continuous se usa para la acción más larga y el past simple para la acción más corta.
We were driving along when suddenly a dog ran out in front of the car.
She sent (past simple) me a text message while I was waiting (past continuous) for her.
| 1. I saw Sofia last week. She her arm while she . 2. I bought a beer and over to the table to join in the conversation. They about football when I sat down. 3. It’s difficult to believe that his time last week we along 5th Avenue in New York a hot dog. 4. It was a beautiful day yesterday. When I left home the sun and the birds . It good to be alive. 5. Suddenly, I out of the car window and I that we past Big Ben and the Houses of Parliament. 6. When I Sandra in the pub last night she Guinness! 7. I my girlfriend while I around Australia. 8. Yesterday, I home to find that my 14-year-old son my best single malt whisky. 9. Simon me that his wife an affair with her Karate instructor. I him to do nothing. 10. While I for the train, someone their hand in my pocket and my iPod. |
CURSO DE INGLES SEGUNDO PERIODO:
INICIE SU CURSO DE ACUERDO CON SU NIVEL.
REMEMBER TO WRITE THIS ACTIVITIES ON
YOUR COPYBOOKS.
AQUI UN RECORDERIS DEL PASADO SIMPLE PLEASE COPY IT IN YOUR CPOYBOOK: ( POR FAAVOR COPIARLO EN SU CUADERNO) |
Simple Past
Pasado Simple | |||
Where were you born?
I was born in South America. |
¿Dónde naciste?
Nací en Sudamérica. |
Were you born in Brazil?
No, I wasn't. I was born in Argentina. |
¿Naciste en Brasil?
No. Nací en Argentina. |
Where did you grow up?
I grew up in Buenos Aires. |
¿Dónde te criaste?
Me crié en Buenos Aires. |
When did you move here?
I moved here eight years ago, when I was in high school. |
¿Cuándo te mudaste aquí?
Me mudé aquí hace ocho años cuando estaba en la escuela secundaria. |
Did you learn Spanish in high school?
No, I didn't. I studied it in college. |
¿Aprendiste español en la escuela secundaria?
No. Lo estudié en la universidad. |
Did you go to college in California?
Yes, I did. I went to college in Los Angeles. |
¿Fuiste a la universidad en California?
Así es. Fui a la universidad en Los Angeles. |
English Exercises > to be exercises > WAS, WERE, THERE WAS, THERE WERE
http://www.eslgamesworld.com/members/games/grammar/present%20tenses/present%20progressive%20hangman.html
 Elige la respuesta correcta.
Elige la respuesta correcta.
 Cambia las frases a su forma negativa siguiendo el ejemplo.
Cambia las frases a su forma negativa siguiendo el ejemplo.
Asocia cada situación relacionada con el mundo de la empresa con su correspondiente término. (si no visualizas correctamente los ejercicios accede al cuaderno online)
 1. |  2. |  3. | ||
 4. |  5. |  6. |
| 1. She speak English very well. 2. - Do you like shopping? - 3. Why come shopping with us tomorrow? 4. France, Italy and Germany are European . 5. - Is that Juan and Cristina's car? - No, is the Ford Fiesta. 6. Sara work yesterday because she was ill. 7. - What ? - He’s having a shower. 8. How many people at the meeting yesterday? 9. Pepito usually to work 10. I think leave her husband! |  |
| Ej. Emma is a teacher. 1. I like Japanese food. 2. She's married. 3. I like vegetables. 4. Pepito likes video games. 5. They live near the beach. 6. My parents smoke. 7. Today is Tuesday. 8. I like horror films. 9. David swims very well. 10. Maria is a doctor. | 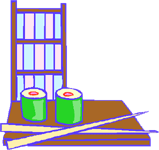
I like Japanese food
|







No comments:
Post a Comment